Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

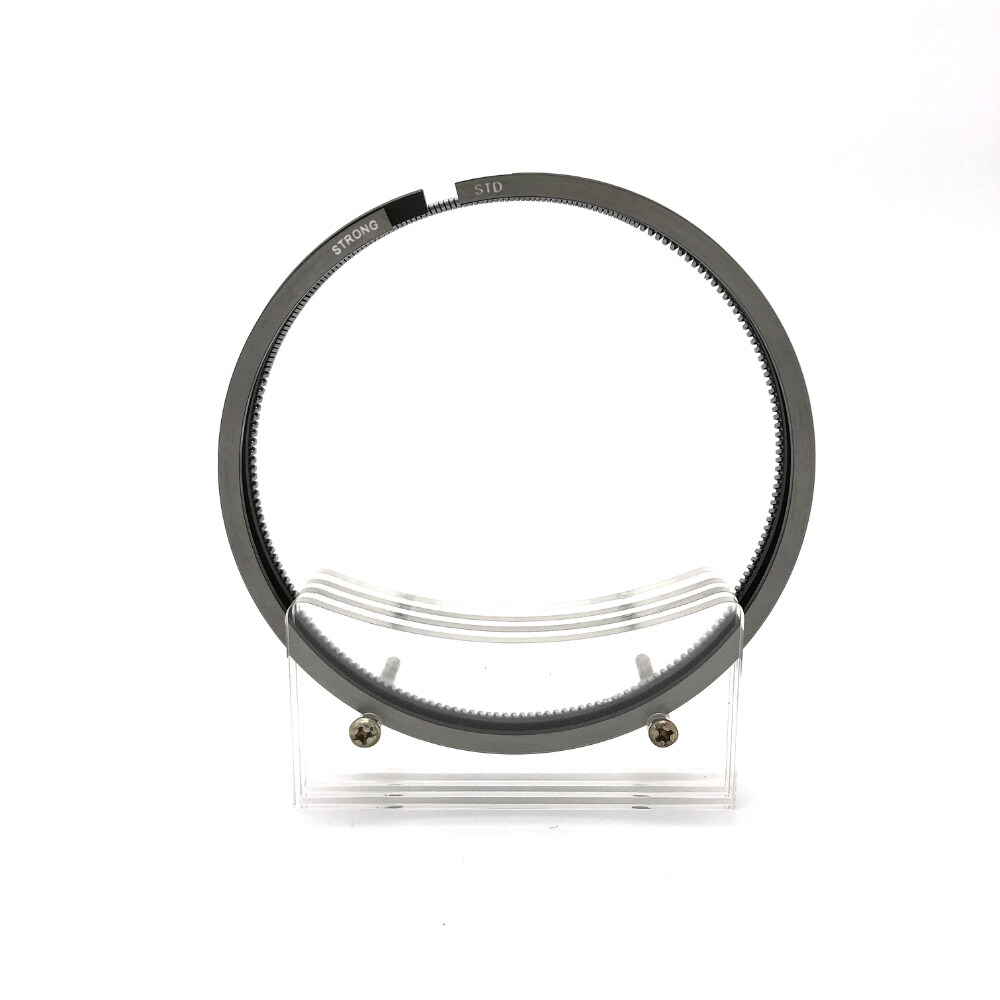
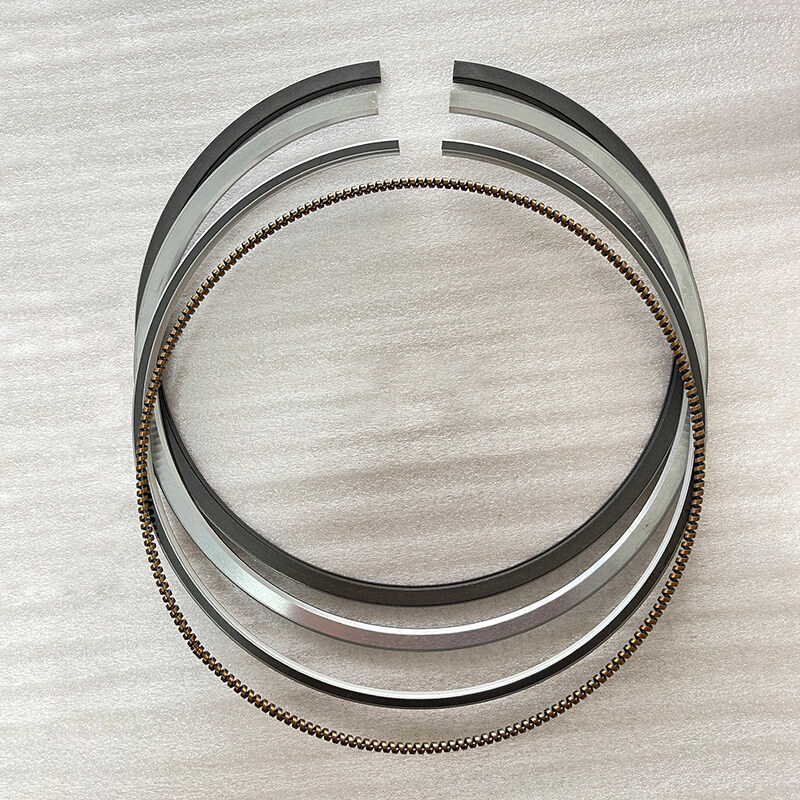
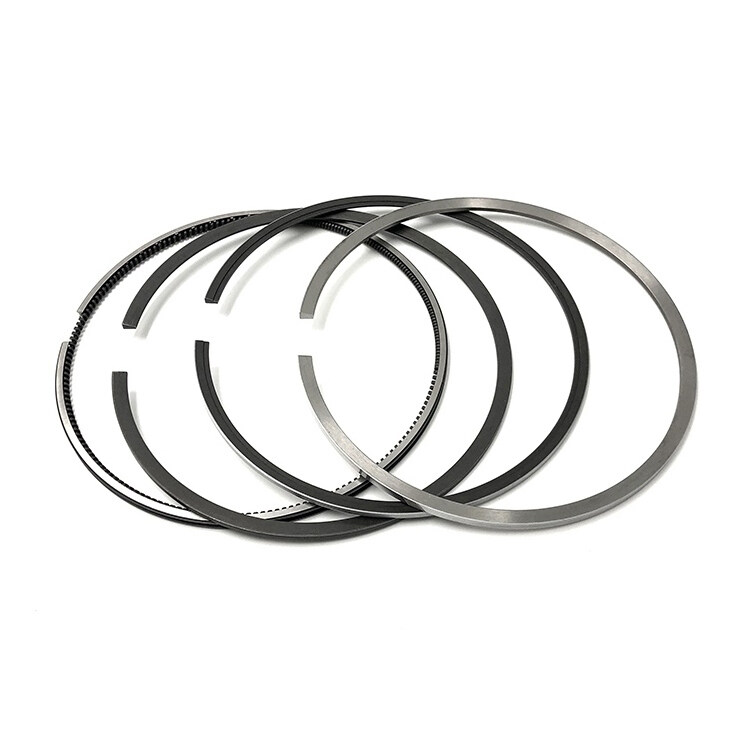
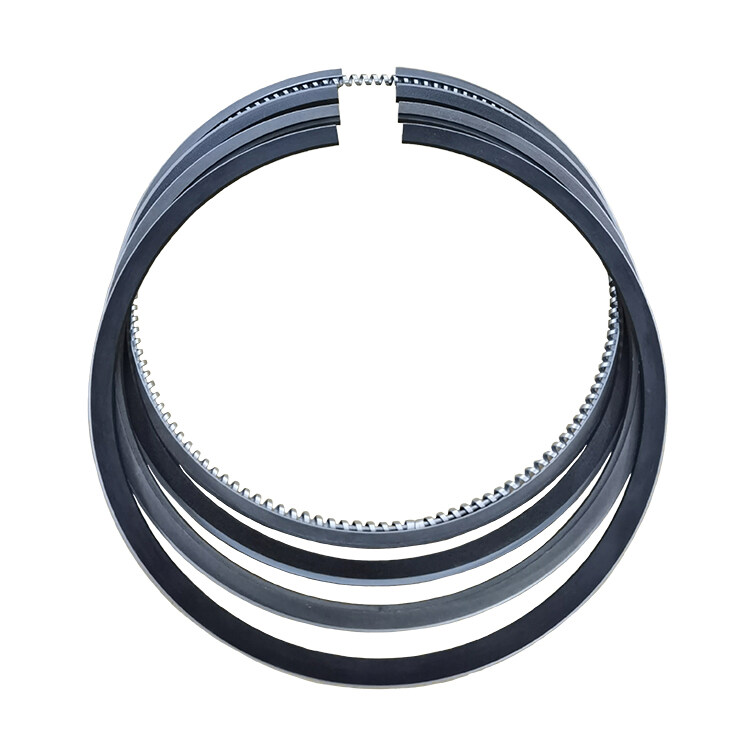
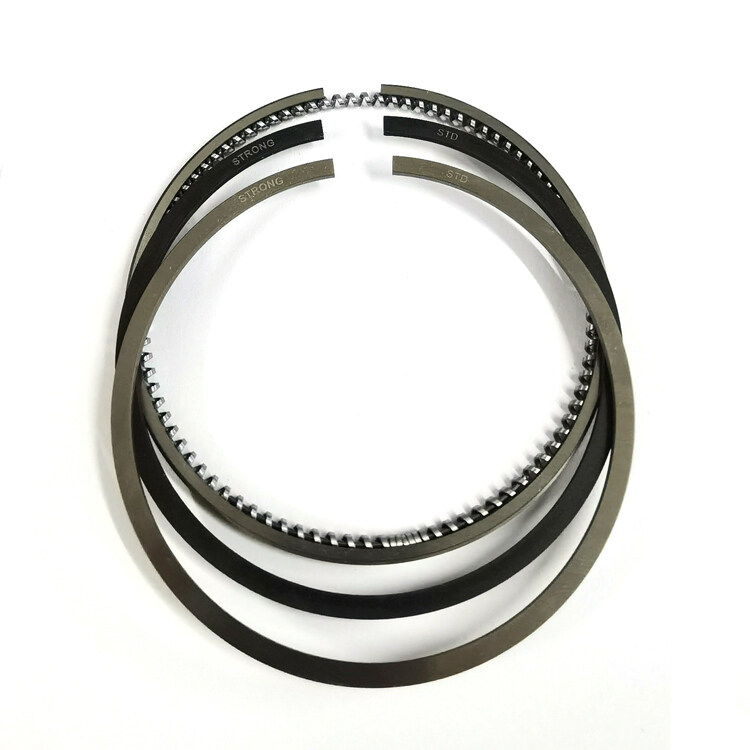
Komatsu 3D84 3 Cylinder 84mm Diesel Engine Piston Ring
Piston rings are crucial components in any internal combustion engine, including the Komatsu 3D84 diesel engine. They play a key role in maintaining proper compression, controlling oil consumption, and promoting efficient combustion
Overview of Komatsu 3D84 Diesel Engine Piston Rings:
Function:
- Piston rings seal the gap between the piston and the cylinder wall. They prevent the escape of combustion gases from the combustion chamber into the crankcase and regulate the distribution of engine oil.
Compression Rings:
- Compression rings are located near the top of the piston and are primarily responsible for sealing the combustion chamber during the compression and power strokes. They maintain compression, ensuring efficient combustion.
Oil Control Rings:
- Oil control rings are typically located below the compression rings and are responsible for regulating the distribution of engine oil along the cylinder wall. They prevent excessive oil from entering the combustion chamber.
Materials:
- Piston rings are often made from high-strength materials, such as cast iron, steel, or advanced materials with good wear resistance. The choice of material depends on the specific engine's requirements and design.
Design:
- The design of piston rings includes precise gaps and grooves to allow for proper expansion and contraction as the piston moves within the cylinder.
The piston ring is crafted with high-strength materials and precision manufacturing techniques, resulting in excellent wear-resistance and a reliable seal between the piston ring and cylinder liner. This seal prevents air leakage and improves the engine’s efficiency and reliability. Each piston ring undergoes rigorous quality testing to ensure its high quality and optimal performance.
Accurate Size Control for Piston Ring Improve the Engine’s Efficiency:
The piston rings undergo high-precision dimensional control to ensure their accuracy and roundness. This precision manufacturing process results in piston rings that fit perfectly within the cylinder liner, improving the engine’s performance and reliability. The accurate and round dimensions of the piston rings ensure that they can withstand the high pressures and temperatures of the engine’s combustion process without causing any damage to the cylinder liner. This feature is essential for maintaining the engine’s efficiency and longevity. The high-precision dimensional control of the piston rings also reduces the risk of oil leakage and improves the engine’s overall sealing performance.
Excellent Tenacity:
The piston rings are highly elastic and have excellent impact toughness. This means that they can withstand the high pressures and temperatures of the engine’s combustion process without deforming or breaking. The elasticity of the piston rings also allows them to conform to the shape of the cylinder liner, ensuring a tight seal and preventing air leakage. The impact toughness of the piston rings ensures that they can withstand the shock and vibration of the engine’s operation without cracking or breaking. This feature is essential for maintaining the engine’s reliability and longevity.
Product Parameter:
|
Product Name |
Piston Ring |
|
Application |
Engineering Machinery Engine |
|
No. of Cyl. |
3 |
|
Bore Diameter |
84.0mm |
|
Size |
2.0+2.0+4.0mm |
|
Material |
Customized |
|
Engine Number |
3D84 |
|
Excavator Number |
PC35R / PC45R |
|
OEM Number |
YM129002-22500 |
|
Car Model |
Yanmar |
|
Condition |
100% Brand-new |
|
Warranty |
6 Months |
|
Packing |
Neutral Packing |
|
Application Industries |
Machinery Repair Shops, Farms, Construction Works |
The Maintenance for 3D84 Engine’s Piston Rings?
- Regularly check the damage of wearing, if you find it has been worn or damaged, please change it on time;
- Regularly check its elasticity and tenacity, once it’s abnormal, please timely change it;
- Please notice the high-speed or low-speed driving and loading, so as to reduce the damage and wearing;
- Prohibit to use engine in terrible environment, such as in high temperature, or highly wet, to maintain its normal operation;
The daily maintenance is also necessary, such as cleaning heat sink or exchanging the air filter.
Product Description
Between the piston and cylinder, the piston ring is a part that is needed for an engine to work efficiently.
Product Features
Characteristics of the piston ring.
Acting force
The force acting on the piston ring are gas pressure, ring itself elasticity, ring reciprocating motion of the inertia force, ring and cylinder and ring groove friction, as shown in the figure. Due to the action of these forces, the ring will produce axial motion, radial motion, rotary motion and other basic motion.
In addition, the piston ring because of its movement characteristics, accompanied by irregular movement, inevitably the axial irregular movement caused by floating suspension and axial vibration, radial irregular movement and vibration, twisting movement, etc.. These irregular movements often prevent the piston ring from functioning. When designing piston rings, give full play to the favorable movement and control the unfavorable side.
Thermal conductivity
The high heat generated by combustion, through the piston ring to the cylinder wall, so can play a role in cooling the piston. Through the piston ring to the cylinder wall to dissipate the heat, generally can reach the top of the piston to bear the heat of 30 to 40%.

Airtightness
The first role of the piston ring is to maintain the seal between the piston and the cylinder wall, control leakage to a minimum. This role is mainly undertaken by the gas ring, that is, the engine in any operating conditions, its compressed air and gas leakage are to be controlled to a minimum, in order to improve thermal efficiency; to prevent air leakage caused by the cylinder and piston or cylinder and ring between the bite; to prevent the deterioration of lubricating oil and caused by failure.
Oil control
The second role of the piston ring is to properly scrape off the slippery oil attached to the cylinder wall, and to maintain normal oil consumption. When the supply of lubricating oil is too much will be sucked to the combustion chamber, so that the oil consumption increases, and due to the combustion of carbon, the engine performance impact is extremely bad.
Support
Because the piston is slightly smaller than the cylinder bore, such as no piston ring, the piston is not stable in the cylinder, it is impossible to move freely. At the same time, the ring also prevents the piston from directly contacting the cylinder, playing a supporting role. Therefore, the piston ring in the cylinder up and down movement, its sliding surface all rely on the ring to bear.
Product Function
Function 1 Seal for combustion gas
Function is to fully maintain in-cylinder airtightness between the piston and cylinder wall.
It works hard to keep a lid on combustion gas leaking into the gap between the piston and cylinder created at the time of an explosion.
If combustion gas leaked, full power could not be realized and fuel consumption would increase, which is detrimental both economically and environmentally.
Function 2 Control lubricating oil (engine oil)
Function to constantly create the minimum required lubricating oil layer to prevent burn.
Inside an engine's cylinder, the piston ring is subject to high-temperature combustion gas, and, with the piston, must travel and return many thousands of times a minute, or even more.
To ensure the piston ring and cylinder do not burn, and to prevent excess lubricating oil getting inside the combustion chamber, the cylinder wall lubricating oil layer is controlled at the minimum required.
Function 3 Heat conduction function
Function that releases heat from the piston to the cylinder.
When the gas explodes, the temperature inside the piston reaches a heat of approximately 300 degrees Centigrade. If that heat remains inside the piston, the engine may be damaged, so that heat must be released from the interior. The piston ring helps to do that.
Function 4 Piston attitude support
Function that prevent the piston making strong contact with the cylinder wall.
If the piston is at an angle, as it moves it makes contact with various places, and this can cause engine damage. The piston ring supports the piston so the piston can travel smoothly up and down.